About the chemical test (關於化學測試)
- Science testing of gemstone are used to determine:
- Nature (Natural or synthetic, 天然或合成)
- Origin (起源)
- Type of gemstones (寶石類型)
- Whether it is treated or not (寶石是否受到處理)
Diamond 鑽石
- Determining type of Diamond (鑽石類型)
Using FTIR ( Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy 傅立葉變換紅外光譜)
- Type I : contain traces of nitrogen (N) as impurities 雜質
- Type II : contain boron (B) as impurities
The diamond are being put inside liquid nitrogen 液態氮 (-196°C), to show a distinct spectra in extreme temperature conditions.
The spectrum above showed a treated diamond of Type Ia in greenish-yellow colour. The peaks 尖峰 are more distinct in extreme temperatures for analyzing.
2. Differentiating natural and synthetic diamonds(天然或合成)
Using Low-Temperature photoluminescence spectra 低溫光致發光光譜 (PL)
The growth of synthetic diamond has a different growth pattern from the natural diamonds. Analyzing the diamond using lasers with different emission wavelengths 發射波長 , to provide characteristic information for treatment detection and nature detection 用於治療檢測和性質檢測.
Gemmologists used previous reference records 先前的參考記錄 of diamonds to determine whether the sample is being treated or synthesized.
Ruby 紅寶石
- Test for Treatment of Ruby(紅寶石處理)
Using FTIR ( Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy 傅立葉變換紅外光譜)
- analyze molecular vibration (non-destructive) 分子振動(非破壞性)
- treated rubies might have other organic molecules (oil, wax, resin 油、蠟、樹脂) to fill in the fissures 填補裂縫
- Different vibration pattern 不同振動模式 compare to an untreated ruby
FTIR spectra of unheated (green) and heated rubies (red), analyze different peak patterns
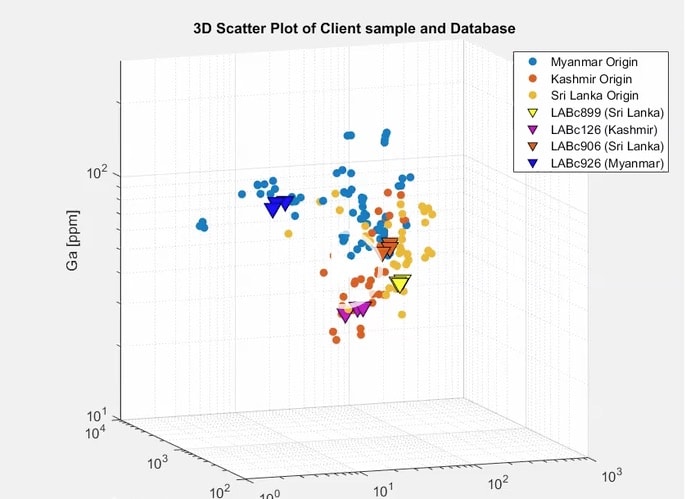
2. Analysis for Origin determination 原產地鑑定
Using Time-of- Flight (GEM-TOF)
Chemical composition of different origin varies, in order to understand whether it comes from marble deposit or other sources大理石礦床或其他來源.
Rubies in marble deposit have lower iron (Fe) than in amphibolite deposit 角閃岩礦床. Using a database to conclude the analysis.
3. Colour grading of Ruby 紅寶石的顏色分級
Using UV-vis spectroscopy 紫外可見光譜
Reveal how much light of each spectral color is absorbed and transmitted by the gemstone.
揭示寶石吸收和透射每種光譜顏色的光量。
Chromium peaks (Cr) are very visible comparing to Iron peaks (Fe).
Sapphire 藍寶石
- Test for Chemical composition and potential origin 化學成分和潛在來源
Using UV-Vis-NIR (Ultraviolet-visible-Near Infrared) spectrophotometry 紫外-可見-近紅外線 分光光度法
- analyze color of sapphire 分析藍寶石的顏色
- chemical composition 化學成分
- potential origin 潛在起源
Observing the absorption band 吸收帶 and peak in UV-Vis spectrum, assess the absorption and transmission pattern 吸收和透射模式
Reveal the presence of color ions : Iron (Fe2+ or Fe3+) and Titanium (Ti4+) and their relative ratios. To determine its characteristics in different geological and geographical origin 決定其不同地質、地理成因的特徵.
2. Analysis for Origin determination 原產地鑑定
Using Trace-element analysis (GEM-TOF) 微量元素分析
By comparing with a reliable database base to identify the country of origin 確定原產國.
Radiometric age dating of surface-reaching inclusions 放射性年齡測定內含物 in sapphires can provide evidence of their origin and offer insights into the geological history spanning millions of years since their formation in host rocks. 提供其起源的證據,並深入了解自其在母岩中形成以來跨越數百萬年的地質歷史
Emerald 祖母綠
- Detection on treated Emerald (祖母綠處理)
Using FTIR analysis 傅立葉變換紅外光譜
The spectral peaks of oil 油 (light green spectrum) and artificial resin 人造樹脂 (dark green spectrum) present in two separate emerald samples illustrate this distinction
2. Origin Determination (原產地鑑定)
a. Using UV-VIS absorption spectroscopy 使用紫外可見吸收光譜法
The chemical composition of an emerald can vary based on its geological origin. Colombian emeralds typically contain higher levels of Chromium (Cr) and vanadium (V) compared to Iron (Fe), while Zambian and Brazilian emeralds exhibit a greater concentration of iron.
祖母綠的化學成分會根據其地質起源而改變。與鐵相比,哥倫比亞祖母綠通常含有較高含量的鉻 (Cr)和釩 (V),而尚比亞和巴西祖母綠則含有較高濃度的鐵。
b. Using GEM-TOF (飛行時間質譜法)
Concentration of chromium, vanadium and iron can reveal information on emerald origin.
鉻(Cr)、釩(V)和鐵(Fe)的濃度可以揭示祖母綠的成因訊息